Introduction: Understanding Age-related Macular Degeneration (AMD)
Age-related macular degeneration (AMD) is a common eye condition that affects the macula, the part of the retina responsible for central vision. It primarily impacts people over 50 and is a leading cause of vision loss in older adults.
Types of AMD:
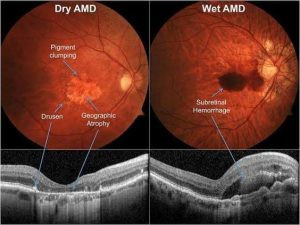
Dry AMD: The more common form, characterized by the thinning of the macula and the presence of drusen (tiny yellow deposits).
Wet AMD: Less common but more severe, involving abnormal blood vessel growth under the retina that can leak fluid or blood.
Causes of AMD:
Age: Can happen to any age
Genetics: Family history can increase risk
Smoking: Significantly raises the likelihood of developing AMD.
High Blood Pressure: Can damage blood vessels in the retina.
Obesity: Associated with a higher risk of AMD progression.
Symptoms of AMD:
- Blurred Central Vision: Difficulty reading or seeing fine details.
- Distorted Vision: Straight lines appear wavy or bent.
- Dark or Empty Areas: In the center of your vision.
- Difficulty Recognizing Faces: Central vision is crucial for face recognition.

Diagnosis of AMD:
Comprehensive Eye Exam: Includes a visual acuity test and dilated eye exam.

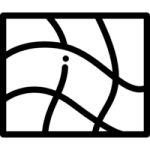
Amsler Grid Test: Detects changes in central vision.
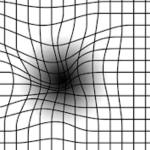
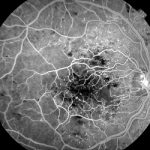
Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT): Provides detailed images of the retina.

Fluorescein Angiography: Highlights abnormal blood vessels in wet AMD.
Treatment:

Dry AMD: Currently, no cure, but certain vitamins and minerals can slow down the progression.
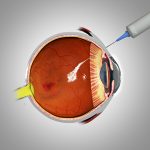
Wet AMD: Anti-VEGF injections to reduce abnormal blood vessel growth, laser therapy, and photodynamic therapy
Preventive Measures:
Regular Eye Exams: Early detection is key.
Healthy Diet: Rich in green leafy vegetables, fish, and nuts.
Quit Smoking: Significantly reduces risk.
Manage Health Conditions: Control blood pressure and cholesterol.
Conclusion:
Age-related macular degeneration is a significant cause of vision loss in older adults, but with early detection and appropriate treatment, its progression can be slowed. Regular eye exams, a healthy lifestyle, and quitting smoking are crucial preventive measures.