What is Retinal Artery Occlusion?
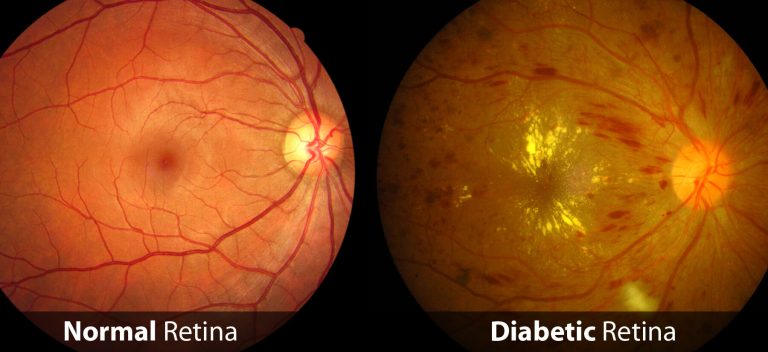
Retinal artery occlusion (RAO) is a serious eye condition where the blood flow to the retina is blocked, leading to sudden vision loss. This is a medical emergency and needs immediate attention.
Types of Retinal Artery Occlusion
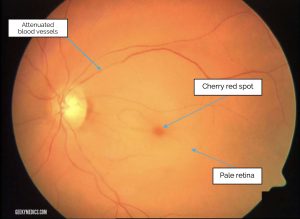
1. Central Retinal Artery Occlusion (CRAO):
- Blockage in the main artery.
- Causes severe vision loss in one eye.
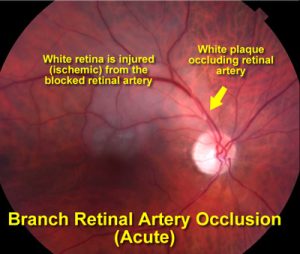
2. Branch Retinal Artery Occlusion (BRAO):
- Blockage in a smaller branch.
- Causes partial vision loss.
Causes of Retinal Artery Occlusion
1. Atherosclerosis: Hardening of the arteries.
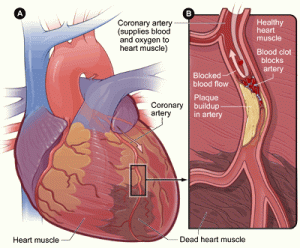
2. Blood Clots: Can form and block the retinal veins.
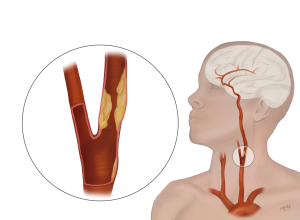
3. Carotid artery disease: Blockages in the neck arteries.
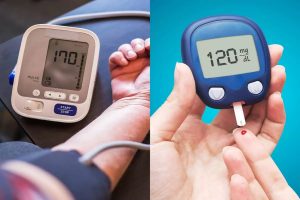
4. Chronic Conditions: High blood pressure, diabetes, and heart disease.
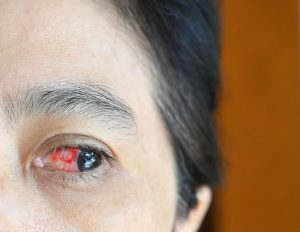
Symptoms of Retinal Artery Occlusion
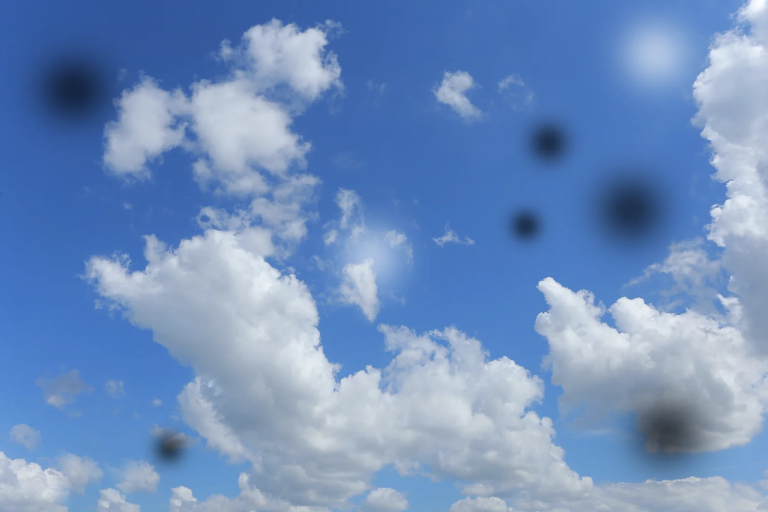
Sudden Vision Loss: Often in one eye.
Blurred Vision: Partial loss of vision or seeing dark spots.
Temporary episodes of vision loss (like a curtain falling over your eye).
Examination
Eye exam to check for RAO signs.
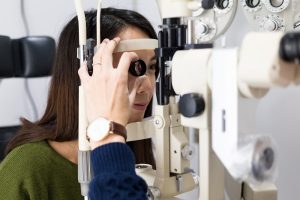
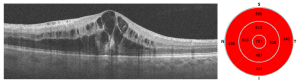
Imaging tests like fluorescein angiography and OCT.
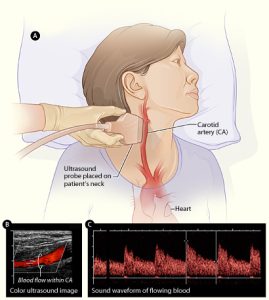
Carotid ultrasound to check neck arteries.
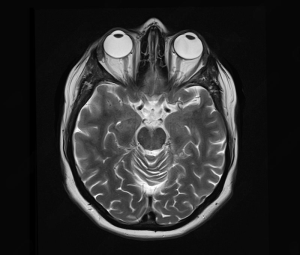
Blood test & MRI to find the root cause of the stroke in the eye
Treatment
Immediate Medical Attention: Time is crucial to restore blood flow.
Medications: To lower eye pressure and dissolve clots.

Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy: Increases oxygen supply to the retina.

Vitrectomy: Surgery to remove the vitreous gel and clear blockages.

Managing Underlying Conditions: Control high blood pressure, diabetes, and cholesterol.

Preventive Measures
Healthy Lifestyle: Balanced diet, regular exercise, and avoiding smoking.

Regular Eye Exams: Essential for early detection and management of RVO and related conditions.
Managing Chronic Conditions: Keep diabetes, high blood pressure, and cholesterol under control.
Conclusion
RAO is a serious condition that needs quick treatment to prevent permanent vision loss. Regular health check-ups and a healthy lifestyle are key to preventing RAO.